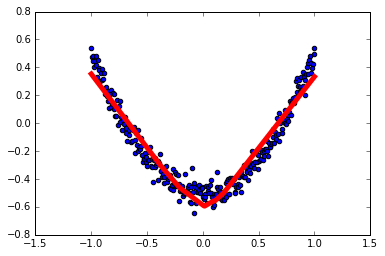
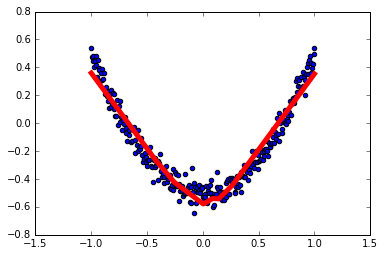
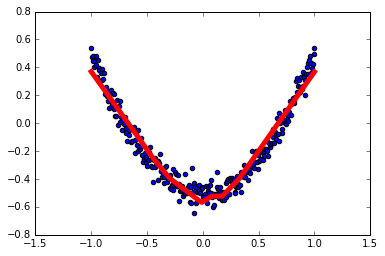
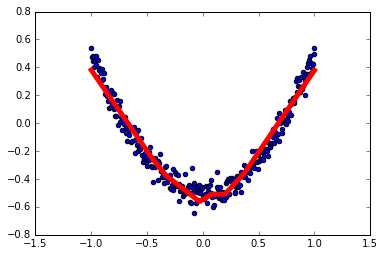
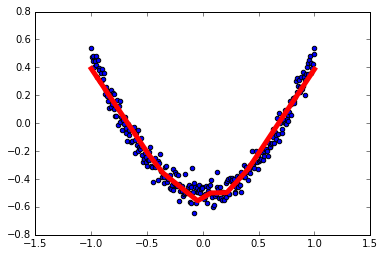
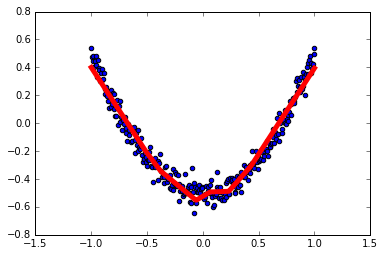
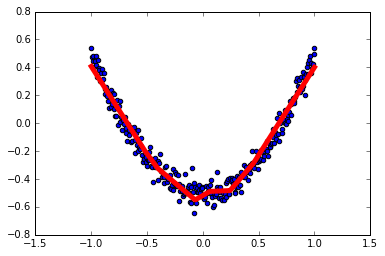
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
|
def add_layer(inputs, in_size, out_size, activation_function=None):
weights = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([in_size, out_size]))
biases = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([1, out_size]) + 0.1)
wx_plus_b = tf.matmul(inputs, weights) + biases
if activation_function is None:
outputs = wx_plus_b
else:
outputs = activation_function(wx_plus_b)
return outputs
x_data = np.linspace(-1, 1, 300)[:, np.newaxis]
noise = np.random.normal(0, 0.05, x_data.shape)
y_data = np.square(x_data) - 0.5 + noise
xs = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 1])
ys = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 1])
l1 = add_layer(xs, 1, 10, activation_function=tf.nn.relu)
prediction = add_layer(l1, 10, 1, activation_function=None)
loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.reduce_sum(tf.square(ys - prediction), reduction_indices=[1]))
train_step = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.1).minimize(loss)
init = tf.initialize_all_variables()
sess = tf.Session()
sess.run(init)
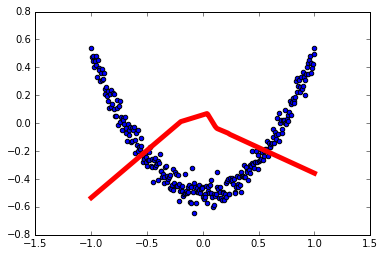
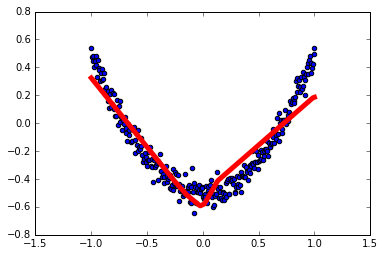
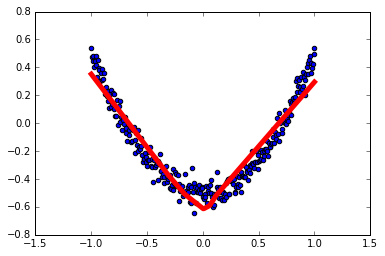
for i in range(1000):
sess.run(train_step, feed_dict={xs: x_data, ys: y_data})
if i % 50 == 0:
print sess.run(loss, feed_dict={xs: x_data, ys: y_data})
|