ORM(Object/Relational Mapper),即“对象-关系型数据映射组件”。对于O/R,即 Object(对象)和Relational(关系型数据),表示必须同时使用面向对象和关系型数据进行开发。本文简述通过 Java 动态代理机制实现关系数据与 POJO 对象的映射。
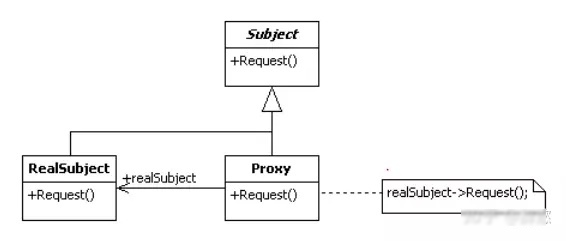
代理 静态代理 静态代理其实就是指设计模式中的代理模式。
静态代理模式在增强现有的接口业务功能方面有很大的优点,但是大量使用这种静态代理,会使我们系统内的类的规模增大,并且不易维护。
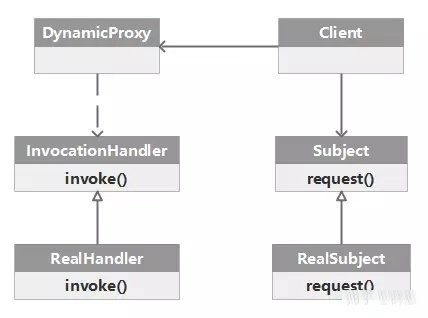
动态代理 为了解决静态代理的问题,引入动态代理的概念,在编译时或者运行时,可以在需要代理的地方动态生成代理,减轻代理类和类在系统中冗余的问题。
Java 动态代理基于经典代理模式,引入了一个 InvocationHandler,InvocationHandler 负责统一管理所有的方法调用。
InvocationHandler InvocationHandler 接口定义:
1 2 3 4 public interface InvocationHandler { public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable; }
每一个动态代理类都必须要实现 InvocationHandler 这个接口,通过代理类的实例调用一个方法时,这个方法的调用就会被转发为由 InvocationHandler 这个接口的 invoke 方法来进行调用。
Proxy Proxy 这个类的作用就是用来动态创建一个代理对象的类,它提供了许多的方法,但是我们用的最多的就是 newProxyInstance 这个方法,可以获得一个动态的代理对象:
1 public static Object newProxyInstance(ClassLoader loader, Class<?>[] interfaces, InvocationHandler h) throws IllegalArgumentException
实现 参照 mybaits 的用法实现基本的映射能力。
注解 首先定义了三个注解,一个作用在类上 DaoMapper 作用在类上标记这是一个映射类,然后定义注解 Selector 作用在方法上标记查询作用,定义注解 Param 作用在参数上为预编译位的映射。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 @Documented @Target(ElementType.TYPE) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) public @interface DaoMapper { } @Documented @Target(ElementType.METHOD) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) public @interface Selector { String value(); } @Documented @Target(ElementType.PARAMETER) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) public @interface Param { String value(); }
定义一个实体类,与数据库的表字段映射上。增强 feature 可以自动做驼峰转换,这里没有实现。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 @Data public class BaseLineModel { public static final String TABLE = "baseline"; private Integer id; private String report_name; private Integer report_period; private LocalDateTime creation_date; }
定义dao层接口,加上注解
1 2 3 4 5 6 @DaoMapper public interface BaseLineDao { @Selector("select * from "+ BaseLineModel.TABLE +" where report_name = #{reportName}") BaseLineModel select(@Param("reportName") String report_name); }
JDBC OP 做到一个很简单的 JDBC 操作工具类,字段映射处理也写到了这里。实现了查询操作,将入参 sql template 以及参数按顺序传入,生成 prepareStatement 后执行,再将返回结果映射到 model 对象。这里的连接池管理、自动重连、配置管理等增强 features 非重点,不做实现。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 /** * 查询 * @param clazz model类 * @param sql * @param params * @param <T> * @return */ public <T> T query(Class<T> clazz, String sql, Object... params) throws SQLException, IllegalAccessException, NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, InstantiationException { Object model = clazz.newInstance(); try (Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/cat", "root", "123456")) { PreparedStatement statement = conn.prepareStatement(sql); int flag = 1; for (Object obj : params) { setValue(statement, flag, obj); flag++; } ResultSet resultSet = statement.executeQuery(); resultSet.afterLast(); resultSet.previous(); fullRes(resultSet, model); } return (T) model; }
映射函数,通过自动寻找 setter 方法填充结果,这里只实现了三种字段。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 private static void fullRes(ResultSet resultSet, Object model) throws SQLException, InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException, NoSuchMethodException { Field[] declaredFields = model.getClass().getDeclaredFields(); for (Field field : declaredFields) { String fieldName = field.getName(); if (fieldName.toUpperCase().equals(fieldName)) { continue; } String setFuncName = "set" + fieldName.substring(0, 1).toUpperCase() + fieldName.substring(1); String fieldType = field.getGenericType().toString(); Object object = resultSet.getObject(fieldName); if (fieldType.equals("class java.lang.String")) { Method m = model.getClass().getMethod(setFuncName, String.class); m.invoke(model, object); } else if (fieldType.equals("class java.lang.Integer")) { Method m = model.getClass().getMethod(setFuncName, Integer.class); m.invoke(model, object); } else if (fieldType.equals("class java.time.LocalDateTime")) { Method m = model.getClass().getMethod(setFuncName, LocalDateTime.class); if (object instanceof Timestamp) { object = ((Timestamp) object).toLocalDateTime(); } m.invoke(model, object); } } }
动态代理部分 定义一个 MapperMethod 类,实例化的时候提取接口方法的注解信息解析成 JDBC 需要的参数以及记录接口方法的返回对象, execute 执行。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 public class MapperMethod<T> { private String sql; private Class<?> resType; private int[] paramsIndex; public MapperMethod(Method method) { this.resType = method.getReturnType(); String sourceSql = method.getAnnotation(Selector.class).value(); Parameter[] parameters = method.getParameters(); int flag = 0; this.paramsIndex = new int[parameters.length]; for (Parameter parameter: parameters) { String paramName = parameter.getAnnotation(Param.class).value(); String paramFullName = String.format("#{%s}", paramName); int indexOf = sourceSql.indexOf(paramFullName); this.paramsIndex[flag] = indexOf; flag++; this.sql = sourceSql.replace(paramFullName, "?"); } } public Object execute(Object[] objects) { JdbcUtil jdbcUtil = new JdbcUtil(); try { return jdbcUtil.query(this.resType, this.sql, objects); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IllegalAccessException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (NoSuchMethodException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (InvocationTargetException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (InstantiationException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return null; } }
定义动态代理类,在实例化的时候记录代理接口,以及代理方法类缓存,调用接口的时候会被动态代理到 invoke 函数执行,然后交由 MapperMethod 代理方法实例执行。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler; import java.lang.reflect.Method; import java.util.Map; import java.util.Objects; public class MapperProxy<T> implements InvocationHandler { private final Class<T> mapperInterface; private final Map<Method, MapperMethod> methodCache; public MapperProxy(Class<T> mapperInterface, Map<Method, MapperMethod> methodCache) { this.mapperInterface = mapperInterface; this.methodCache = methodCache; } @Override public Object invoke(Object o, Method method, Object[] objects) throws Throwable { MapperMethod mapperMethod = cachedMapperMethod(method); return mapperMethod.execute(objects); } private MapperMethod cachedMapperMethod(Method method) { MapperMethod mapperMethod = methodCache.get(method); if (Objects.isNull(mapperMethod)) { mapperMethod = new MapperMethod(method); methodCache.put(method, mapperMethod); } return mapperMethod; } }
最后代理工厂类,接收被 DaoMapper 作用的接口,并通过 newInstance 方法创建代理类实例。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 public class MapperProxyFactory<T> { private final Class<T> mapperInterface; private Map<Method, MapperMethod> methodCache = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(); public MapperProxyFactory(Class<T> mapperInterface) { if (Objects.isNull(mapperInterface.getAnnotation(DaoMapper.class))) { throw new RuntimeException("缺少注解 DaoMapper"); } this.mapperInterface = mapperInterface; } public T newInstance() { final MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy = new MapperProxy<>(mapperInterface, methodCache); return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(mapperInterface.getClassLoader(), new Class[]{mapperInterface}, mapperProxy); } }
执行,创建一个代理工厂,然后创建 BaseLineDao 的代理对象, 调用 select 方法,实际上调用到代理对象的 invoke 方法,然后交由 mapperMethod.execute 方法执行:
1 2 3 4 5 6 public static void main(String[] args) { MapperProxyFactory mapperProxyFactory = new MapperProxyFactory(BaseLineDao.class); BaseLineDao baseLineDao = (BaseLineDao) mapperProxyFactory.newInstance(); BaseLineModel test1 = baseLineDao.select("TEST1"); System.out.println(test1); }
扩展 TODO:
Java动态代理与 cglib 动态代理的异同点。
动态代理的实现原理。
总结 通过这个个简单的实践,了解了 Java 动态代理的使用方法以及对象关系数据的映射处理。
参考
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/60805342 https://www.zhihu.com/question/20794107/answer/658139129